In the previous article, we have systematically organized the basic knowledge architecture of microcarriers and made a preliminary explanation of their classification. As a key technological innovation in the field of cell culture, microcarriers provide an ideal microenvironment for cell adhesion, growth and proliferation by virtue of their excellent three-dimensional support properties, which significantly improves the efficiency and quality of cell culture. However, there are many types of microcarriers, and the physical and chemical properties of microcarriers made of different materials differ significantly, which directly determine their applicability and limitations in specific application scenarios. In this paper, we will focus on the various types of microcarriers made of different materials, analyze their unique performance, and comprehensively evaluate their advantages and disadvantages, in the hope of providing scientific evidence and support for the selection of appropriate microcarriers.
1. Large specific surface area: these microcarriers have a great specific surface area, which makes it possible to cultivate more cells per unit volume of culture medium and increase the cell yield.
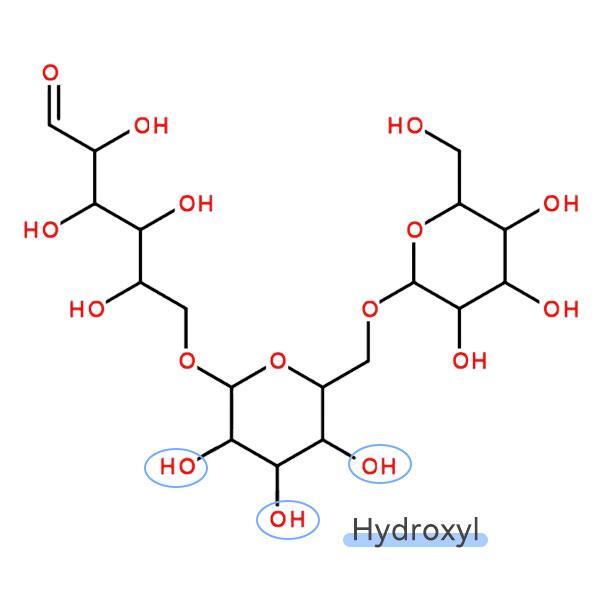
2. Good biocompatibility: glucan is a natural biopolymer, made of glucose monomers connected by glycosidic bonds, has good biocompatibility, low toxicity to cells and organisms, generally does not cause immune response or other adverse physiological reactions, is conducive to the adhesion, growth and proliferation of cells, and is widely used in the fields of drug delivery, cell culture and tissue repair.
3. Strong chemical modification: glucan molecules contain abundant hydroxyl and other active groups, which can be chemically modified to introduce various functional groups, such as targeting groups, drug binding sites, hydrophilic or hydrophobic groups, etc., so as to realize the functional customization of the microcarriers to meet different application requirements, such as improving drug loading, achieving targeted drug delivery, enhancing the adhesion ability of the cells, and so on.
 Disadvantage(Dis):
Disadvantage(Dis):
1. Separation difficulties: dextran-based microcarriers have strong adhesion to the inner wall of the bioreactor after dissolution, and it is not easy to effectively digest and separate the cells from the microcarriers after large-scale microcarrier cell culture, making it difficult to realize efficient and high-yield recovery of cells.
2. Increase the production cost and process complexity: At present, trypsin digestion is generally used for separation, and dextranase can also be used to degrade the microcarrier in the small-scale culture stage, which brings a greater waste of cell recycling and some technical obstacles to the process amplification, and increases the cost of production and the complexity of the process.
3. Stability problems in some situations: Under some extreme conditions, such as strong acid, strong alkali, high temperature or high salt concentration, dextran-based microcarriers may undergo structural changes, changes in degradation rate or loss of function, thus limiting their application in some special environments.
Ad:
1. Biocompatibility: Gelatin is a biocompatible material, mainly of porcine origin or bovine origin, almost non-toxic to human body. Gelatin matrix microcarriers are based on cross-linked gelatin proteins. Gelatin is characterized by biocompatibility, microporosity, non-rigidity, non-toxicity, good activity, easy degradation and recyclability. The large specific surface area can satisfy the large-scale culture of mammalian cells, and it has good bearing effect for both wall-dependent cells and suspension culture cells.
2. Biodegradability: in the organism or in a specific environment, gelatin can be gradually degraded, and its degradation products are usually some non-toxic amino acids and other small molecules, which can be metabolized and absorbed by the organism, and won't remain in the body for a long period of time, which reduces the potential hazards to the organism, which makes gelatin microcarriers have a great advantage in the fields of drug slow release and tissue engineering.
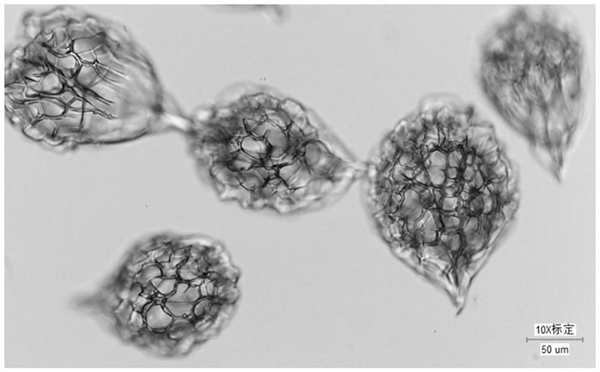 3. Porous structure: The gelatin-based macroporous spherical microcarriers are characterized by porosity, which increases the culture surface area, provides more adhesion sites and growth space for cells, and enables cells to obtain a relatively stable growth environment inside the carriers and reduces the influence of external factors on the cells.
3. Porous structure: The gelatin-based macroporous spherical microcarriers are characterized by porosity, which increases the culture surface area, provides more adhesion sites and growth space for cells, and enables cells to obtain a relatively stable growth environment inside the carriers and reduces the influence of external factors on the cells.
Dis:
1. Exogenous components: gelatin microcarriers of animal origin These contaminants may adversely affect cell culture. If the source animal species or extraction process of gelatin is not appropriate, it may carry viruses, bacteria or other microbial contaminants, which may trigger an immune response, leading to immune activation of the cells or produce an inflammatory response, affecting the normal growth and function of the cells, especially in some sensitive to immune response to cell culture or in vivo application scenarios need to pay special attention to.
2. Batch variation: Due to the different sources and extraction methods of animal-derived gelatin, as well as the influence of some factors in the preparation process, there may be batch-to-batch inconsistency, which can affect the reproducibility of cell culture and the consistency of results.
3. Cost issues: Animal-derived gelatin microcarriers are usually more expensive, which may increase the cost of cell culture.
Ad:
1. Non-toxic and biodegradable: cellulose matrix microcarrier is composed of 100% cellulose, which is non-toxic to cells and biodegradable.
2. Microporous structure: composed of cross-linked cellulose, it has a microporous structure with high hardness, which makes it easy for the cells to enter into the microcarrier after inoculation, and increases the surface area of cell culture while reducing the mechanical damage to the cells caused by shear force.
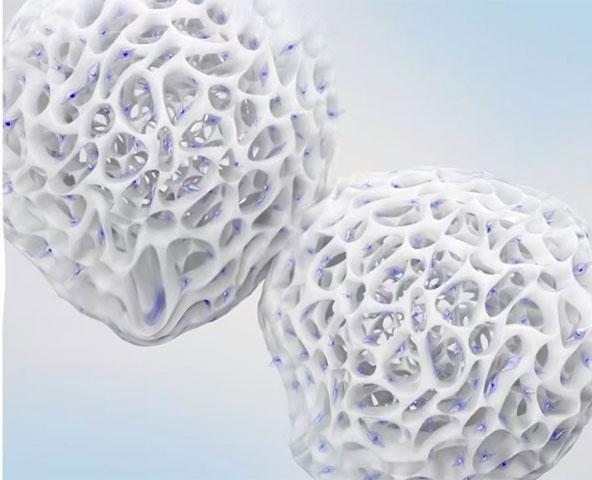
3. High-density cell culture: As the cells are well protected inside the microcarrier, it is possible to increase the aeration and stirring speed, use a higher concentration of carriers, and carry out high-density culture.
Dis:
1. Difficulty of on-line monitoring and analysis: Since the cells mostly grow inside the wells, it is not conducive to direct on-line monitoring and analysis of the cells.
2. Difficulty in cell harvesting: cells grow inside the hole, which also increases the difficulty of cell harvesting.
Ad:
1. High transparency: polystyrene has good optical transparency, which makes it easy to observe the growth of cells on the surface of the microcarrier under the microscope and monitor the growth status of cells.
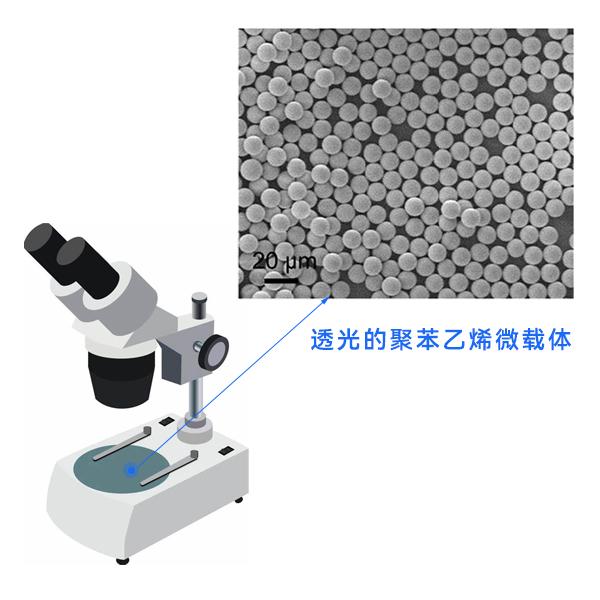 2. No adsorption of serum: polystyrene microcarriers do not adsorb serum, which helps to harvest the special metabolites of the cells, and at the same time reduces the uptake of nutrients in the culture medium, making the utilization rate of the medium higher.
2. No adsorption of serum: polystyrene microcarriers do not adsorb serum, which helps to harvest the special metabolites of the cells, and at the same time reduces the uptake of nutrients in the culture medium, making the utilization rate of the medium higher.
3. Reusable: After appropriate treatment, polystyrene microcarriers can be reused, which reduces the cost of cell culture.
4. Adjustable surface properties: Polymer microspheres are obtained by chemical or physical means, and the surface is covered with some protein coatings or functional groups, and the surface properties, such as charge distribution, hydrophilicity, roughness, etc., can also be altered to meet the specific requirements of different cell types on the surface of the substrate and to enhance the adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation effects of the cells.
Dis:
1. Limited biocompatibility: Polystyrene is a synthetic polymer, which may lack some bioactive molecules and signals, which may have certain effects on the long-term growth and functional maintenance of cells, and may be limited in some cell culture applications that require very high biocompatibility.
2. Relatively weak cell adhesion: polystyrene itself has certain hydrophobicity, and its adhesion may be insufficient for some cell types, requiring complex modification or pretreatment of the microcarrier surface, increasing the complexity and cost of experimental operations.
 3. Unsuitable for primary cell culture: due to, polystyrene microcarriers may not be suitable for primary cell culture.
3. Unsuitable for primary cell culture: due to, polystyrene microcarriers may not be suitable for primary cell culture.
4. Risk of cell damage: During the culture process, the cells may be damaged due to the slow wall affixation speed and the collision generated by the rigid structure and agitation of the microcarriers.
Ad:
1. No animal-derived components: polyester fiber microcarriers have no animal-derived components, high biosafety.
2. Good chemical stability: polyester fiber has excellent acid and alkali resistance and heat resistance, in the common environment of cell culture, such as different pH, temperature and medium composition conditions, can maintain its chemical structure and performance stability, not easy to degradation, deformation, or chemical reaction with the components in the medium, so as to provide a stable physical support and chemical environment for cell culture.
3. Three-dimensional mesh structure: polyester fiber microcarriers are generally diamond-shaped or sheet fan leaf type, some with three-dimensional mesh space three-dimensional structure, which can provide cells with a larger growth space and more adhesion sites.
4. Reduce the impact of shear: due to its multi-layer tension structure, stirring shear and aeration bubbles generated by the cell growth does not affect the growth of cells, cell growth is similar to the static state of the rotating bottle, which ensures that the culture medium and the cells are in full contact with each other.
Dis:
1. Insufficient adhesion: polyester fiber itself is highly hydrophobic, has low surface energy and does not possess cell recognition sites, which may affect cell adhesion and growth. In the late stage of culture, the cells may also fall off from the polyester fiber matrix microcarrier, affecting the efficiency and purity of cell harvesting.
2. Difficulty in real-time monitoring: The cell growth status cannot be monitored in real time during the culture process, and the cells are located deep in the fiber microstructure, which may lead to insufficient supply of nutrients and oxygen, and uneven cell growth.
3. Separation difficulty: the separation between polyester fiber matrix microcarriers and cells may be difficult, especially when the cell clustering phenomenon is serious, which will increase the complexity and labor intensity of cell harvesting.
In summary, the characteristics of different types of microcarriers determine their diverse application prospects in cell culture. When choosing microcarriers, we need to consider factors such as cell type, culture conditions, cost and final application requirements. In the future, we expect that through interdisciplinary collaboration, we can further break through the existing technological bottlenecks and develop more efficient, safe, and cost-effective microcarriers, which will promote the continuous progress in the fields of cell therapy, tissue engineering, and biopharmaceuticals.
Here is the Holves brand website, https://www.bjholves.com/. Providing different types of industry information, technical knowledge, and solutions, we have developed and produced several new laboratory fermenter, bioreactor, tangential flow filtration system and other equipment to meet your needs from experimental to industrial production.
-
Glucose microcarrier
1. Large specific surface area: these microcarriers have a great specific surface area, which makes it possible to cultivate more cells per unit volume of culture medium and increase the cell yield.
2. Good biocompatibility: glucan is a natural biopolymer, made of glucose monomers connected by glycosidic bonds, has good biocompatibility, low toxicity to cells and organisms, generally does not cause immune response or other adverse physiological reactions, is conducive to the adhesion, growth and proliferation of cells, and is widely used in the fields of drug delivery, cell culture and tissue repair.
3. Strong chemical modification: glucan molecules contain abundant hydroxyl and other active groups, which can be chemically modified to introduce various functional groups, such as targeting groups, drug binding sites, hydrophilic or hydrophobic groups, etc., so as to realize the functional customization of the microcarriers to meet different application requirements, such as improving drug loading, achieving targeted drug delivery, enhancing the adhesion ability of the cells, and so on.

1. Separation difficulties: dextran-based microcarriers have strong adhesion to the inner wall of the bioreactor after dissolution, and it is not easy to effectively digest and separate the cells from the microcarriers after large-scale microcarrier cell culture, making it difficult to realize efficient and high-yield recovery of cells.
2. Increase the production cost and process complexity: At present, trypsin digestion is generally used for separation, and dextranase can also be used to degrade the microcarrier in the small-scale culture stage, which brings a greater waste of cell recycling and some technical obstacles to the process amplification, and increases the cost of production and the complexity of the process.
3. Stability problems in some situations: Under some extreme conditions, such as strong acid, strong alkali, high temperature or high salt concentration, dextran-based microcarriers may undergo structural changes, changes in degradation rate or loss of function, thus limiting their application in some special environments.
-
Gelatin microcarrier
Ad:
1. Biocompatibility: Gelatin is a biocompatible material, mainly of porcine origin or bovine origin, almost non-toxic to human body. Gelatin matrix microcarriers are based on cross-linked gelatin proteins. Gelatin is characterized by biocompatibility, microporosity, non-rigidity, non-toxicity, good activity, easy degradation and recyclability. The large specific surface area can satisfy the large-scale culture of mammalian cells, and it has good bearing effect for both wall-dependent cells and suspension culture cells.
2. Biodegradability: in the organism or in a specific environment, gelatin can be gradually degraded, and its degradation products are usually some non-toxic amino acids and other small molecules, which can be metabolized and absorbed by the organism, and won't remain in the body for a long period of time, which reduces the potential hazards to the organism, which makes gelatin microcarriers have a great advantage in the fields of drug slow release and tissue engineering.

Dis:
1. Exogenous components: gelatin microcarriers of animal origin These contaminants may adversely affect cell culture. If the source animal species or extraction process of gelatin is not appropriate, it may carry viruses, bacteria or other microbial contaminants, which may trigger an immune response, leading to immune activation of the cells or produce an inflammatory response, affecting the normal growth and function of the cells, especially in some sensitive to immune response to cell culture or in vivo application scenarios need to pay special attention to.
2. Batch variation: Due to the different sources and extraction methods of animal-derived gelatin, as well as the influence of some factors in the preparation process, there may be batch-to-batch inconsistency, which can affect the reproducibility of cell culture and the consistency of results.
3. Cost issues: Animal-derived gelatin microcarriers are usually more expensive, which may increase the cost of cell culture.
-
Cellulose microcarriers
Ad:
1. Non-toxic and biodegradable: cellulose matrix microcarrier is composed of 100% cellulose, which is non-toxic to cells and biodegradable.
2. Microporous structure: composed of cross-linked cellulose, it has a microporous structure with high hardness, which makes it easy for the cells to enter into the microcarrier after inoculation, and increases the surface area of cell culture while reducing the mechanical damage to the cells caused by shear force.

Dis:
1. Difficulty of on-line monitoring and analysis: Since the cells mostly grow inside the wells, it is not conducive to direct on-line monitoring and analysis of the cells.
2. Difficulty in cell harvesting: cells grow inside the hole, which also increases the difficulty of cell harvesting.
-
Polystyrene microcarriers
Ad:
1. High transparency: polystyrene has good optical transparency, which makes it easy to observe the growth of cells on the surface of the microcarrier under the microscope and monitor the growth status of cells.

3. Reusable: After appropriate treatment, polystyrene microcarriers can be reused, which reduces the cost of cell culture.
4. Adjustable surface properties: Polymer microspheres are obtained by chemical or physical means, and the surface is covered with some protein coatings or functional groups, and the surface properties, such as charge distribution, hydrophilicity, roughness, etc., can also be altered to meet the specific requirements of different cell types on the surface of the substrate and to enhance the adhesion, proliferation, and differentiation effects of the cells.
Dis:
1. Limited biocompatibility: Polystyrene is a synthetic polymer, which may lack some bioactive molecules and signals, which may have certain effects on the long-term growth and functional maintenance of cells, and may be limited in some cell culture applications that require very high biocompatibility.
2. Relatively weak cell adhesion: polystyrene itself has certain hydrophobicity, and its adhesion may be insufficient for some cell types, requiring complex modification or pretreatment of the microcarrier surface, increasing the complexity and cost of experimental operations.

4. Risk of cell damage: During the culture process, the cells may be damaged due to the slow wall affixation speed and the collision generated by the rigid structure and agitation of the microcarriers.
-
Polyester fiber microcarriers
Ad:
1. No animal-derived components: polyester fiber microcarriers have no animal-derived components, high biosafety.
2. Good chemical stability: polyester fiber has excellent acid and alkali resistance and heat resistance, in the common environment of cell culture, such as different pH, temperature and medium composition conditions, can maintain its chemical structure and performance stability, not easy to degradation, deformation, or chemical reaction with the components in the medium, so as to provide a stable physical support and chemical environment for cell culture.
3. Three-dimensional mesh structure: polyester fiber microcarriers are generally diamond-shaped or sheet fan leaf type, some with three-dimensional mesh space three-dimensional structure, which can provide cells with a larger growth space and more adhesion sites.
4. Reduce the impact of shear: due to its multi-layer tension structure, stirring shear and aeration bubbles generated by the cell growth does not affect the growth of cells, cell growth is similar to the static state of the rotating bottle, which ensures that the culture medium and the cells are in full contact with each other.
Dis:
1. Insufficient adhesion: polyester fiber itself is highly hydrophobic, has low surface energy and does not possess cell recognition sites, which may affect cell adhesion and growth. In the late stage of culture, the cells may also fall off from the polyester fiber matrix microcarrier, affecting the efficiency and purity of cell harvesting.
2. Difficulty in real-time monitoring: The cell growth status cannot be monitored in real time during the culture process, and the cells are located deep in the fiber microstructure, which may lead to insufficient supply of nutrients and oxygen, and uneven cell growth.
3. Separation difficulty: the separation between polyester fiber matrix microcarriers and cells may be difficult, especially when the cell clustering phenomenon is serious, which will increase the complexity and labor intensity of cell harvesting.
In summary, the characteristics of different types of microcarriers determine their diverse application prospects in cell culture. When choosing microcarriers, we need to consider factors such as cell type, culture conditions, cost and final application requirements. In the future, we expect that through interdisciplinary collaboration, we can further break through the existing technological bottlenecks and develop more efficient, safe, and cost-effective microcarriers, which will promote the continuous progress in the fields of cell therapy, tissue engineering, and biopharmaceuticals.
Here is the Holves brand website, https://www.bjholves.com/. Providing different types of industry information, technical knowledge, and solutions, we have developed and produced several new laboratory fermenter, bioreactor, tangential flow filtration system and other equipment to meet your needs from experimental to industrial production.
